Rechargeable batteries
We present here a brief overview of rechargeable batteries.
The consumer type is represented by cylinder Ni-MH type with voltage 1.2V. Often it is used instead of alkaline in spite of lower voltage. Ni-MH batteries also is used in some specific industrial applications. There are high power version (D-size cell provide current up to 150A), high temperature version (+90…+100℃), version with full industrial temperature range (-40…+85℃), version which can be charged at negative temperature, etc. Unlike lithium Ni-MH battery from several cells doesn’t need electronic protection and equilibrium circuit, simple fuse is enough. Main disadvantage – low energy density ~ 80 Wh/kg
New trend – lithium 1.5V rechargeable batteries with USB charging. Really battery consists of 3.7V li-ion cell and small PCB with DC/DC converter.
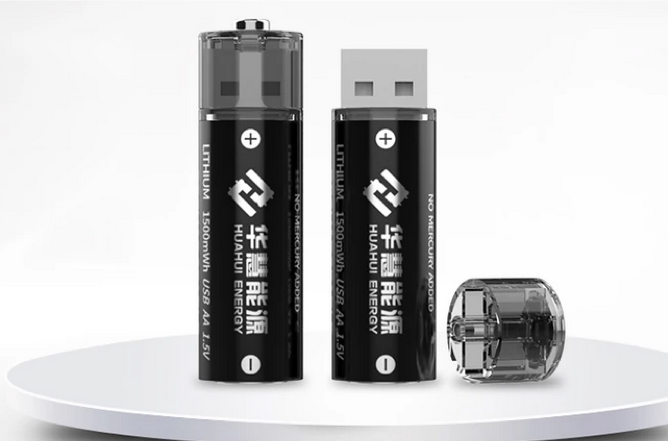
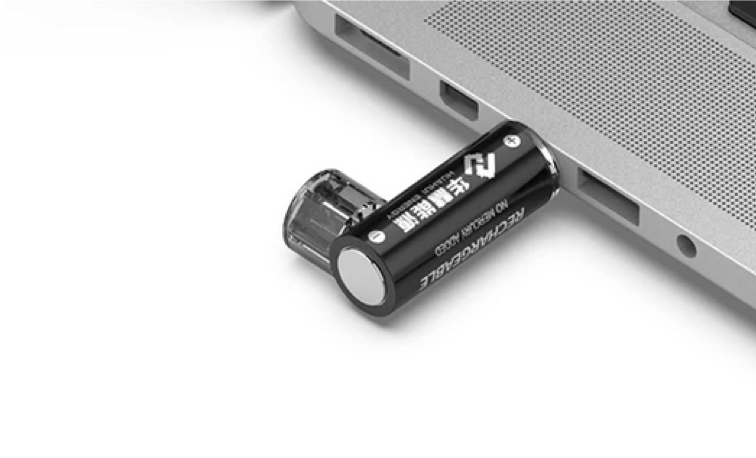
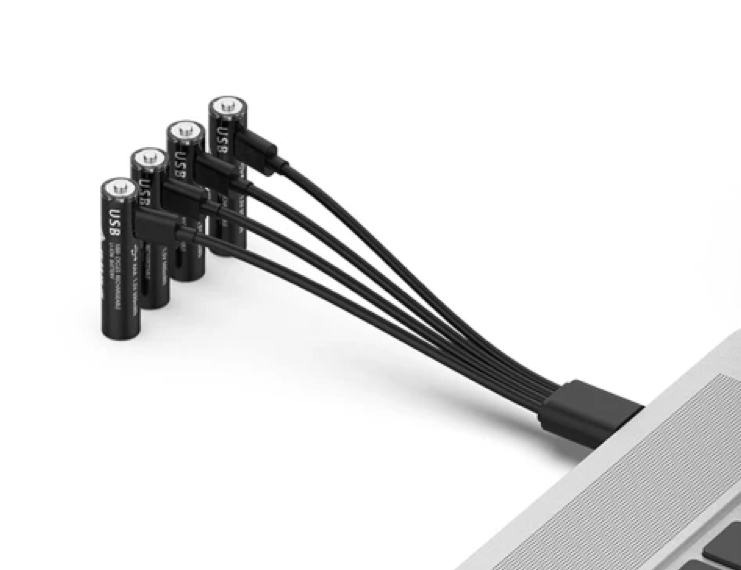




Li-Ion classification by chemistry
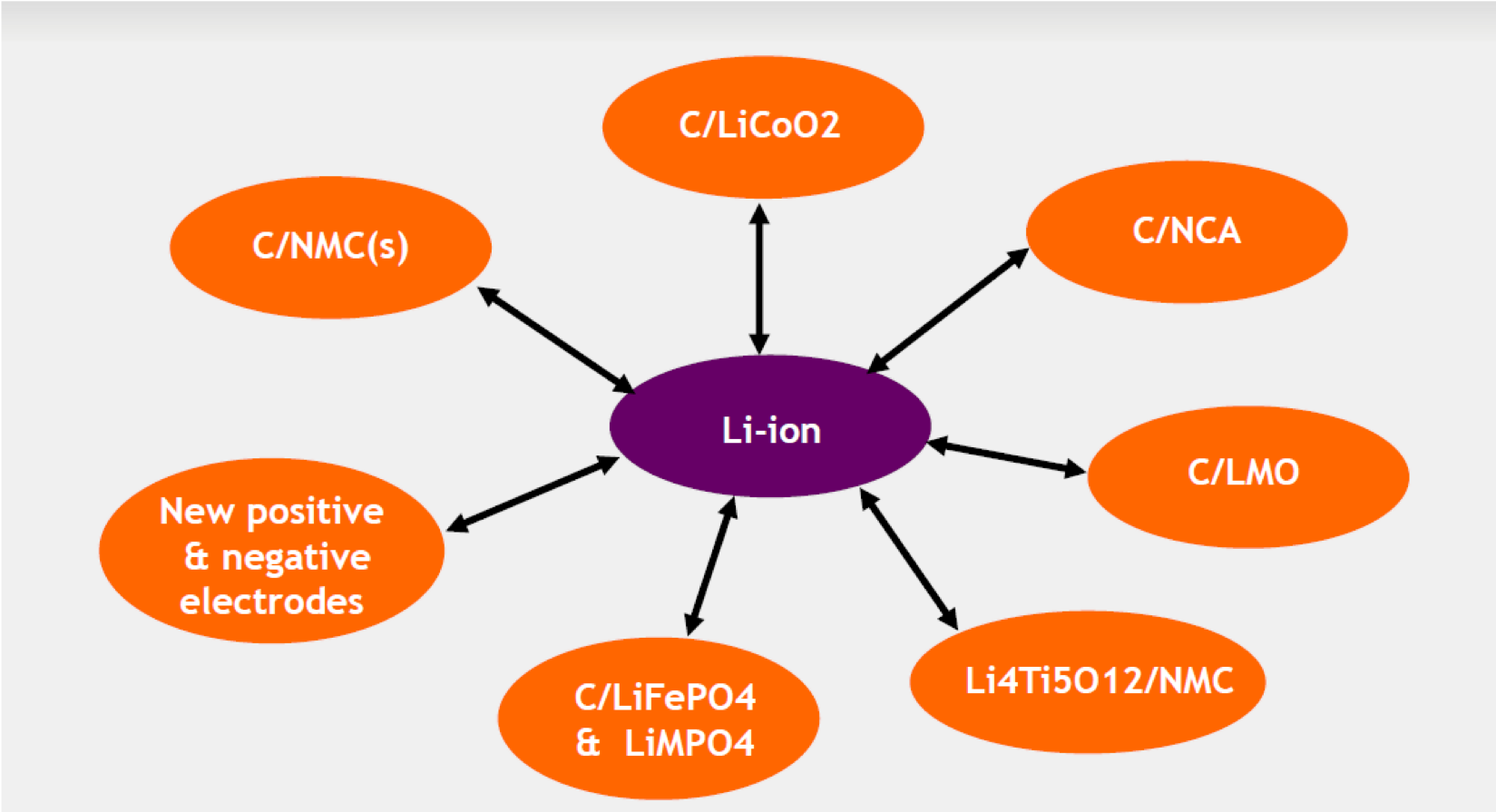
“Li-Ion” classification by cell voltage
| Chemistry | Name, abbreviations | Nominal voltage | Voltage of 100% charged cell |
| {C} +NMC // NCA // LCO // LMO | Li-ion “classic” NMC, NCA, LCO, ICR, INR |
3.6 -3.7V | 4.2– 4.4 V |
| {C} + LFP (Li-FePO4) | Li-FePO4 LFP, IFR |
3.2 - 3.3V | 3.6 - 3.65 V |
| LTO + {LCO // LMO // NMC} | Lithium-Titanate LTO |
2.3 – 2.4 V | 2.7 - 2.8 V |
Features of “Li-Ion” types
| Chemistry abbreviations | Energy density | Number of cycles charge/discharge | Safety |
| NMC/NCA/LCO | 200-300Wh/kg | 500 –3000 | Moderate |
| LFP | 120-200 Wh/kg | 1500 - 7000 | Safe |
| LTO | 80-90Wh/kg | 10000 - 20000 | Safe |